Abstract
Research overview and methodology
This project develops a reproducible hybrid machine learning–econometrics pipeline for program-level analysis across heterogeneous institutional settings. The framework emphasizes transparent feature construction, identification-aware modeling, and systematic robustness diagnostics across multiple specifications. Empirical evaluation focuses on cross-model comparability, stability under alternative assumptions, and interpretability of estimated effects. The full pipeline is designed to support rigorous analysis, replication, and extension.
Project Artifacts
Explore detailed documentation and analysis summaries
System Architecture
Explore the modular workflow and diagnostic framework that powers our reproducible research pipeline
System Architecture
Data Engineering & Harmonization Layer
Deterministic preprocessing, harmonization, train-index enforcement
Stability & Quality-Control Gate
Missingness, variance, and structural integrity checks
Hybrid Modeling Layer
FE · Clustered OLS · ElasticNet (triangulated estimation)
Diagnostics & Validation Engine
Nonlinearity, influence, SHAP, rolling forecasts
Artifact & Reproducibility Manager
Metadata, manifests, model artifacts, logs
The architecture consists of a deterministic, modular workflow that moves from data engineering and stability validation to hybrid modeling, diagnostic evaluation, and artifact management. Each layer communicates through structured, version-controlled outputs, ensuring reproducibility, transparent auditing, and methodological consistency across the entire empirical pipeline.
System Pipeline
RAW DATA INGESTION & LOADING
WDI & WGI retrieval, validation, schema alignment
IDENTIFIER & VARIABLE HARMONIZATION
ISO3 normalization, year indexing, indicator mapping
DETERMINISTIC PREPROCESSING
Imputation, coercion, outlier handling, feature screening
STANDARDIZATION & SCALER PERSISTENCE
Train-sample fit-transform, persisted scaler metadata
TRAIN-INDEX CONSTRUCTION
Deterministic row filtering, FE/OLS/EN parity
MODEL ORCHESTRATION
FE, clustered OLS, ElasticNetCV, triangulated estimation
DIAGNOSTICS & VALIDATION
Nonlinearity, influence, SHAP, rolling forecasts
ARTIFACT EXPORT & REPRODUCIBILITY
Models, metadata, logs, figures, manifests
A deterministic workflow that converts raw macroeconomic indicators into harmonized, standardized, and model-ready datasets before orchestrating hybrid estimation, diagnostics, and forecasting. Each stage exports structured artifacts, enabling reproducible analysis across all model classes
System Diagnostics
Model Output
Predictions, residuals, standardized coefficients
Diagnostics Engine
Unified framework for structural and statistical validation
Nonlinearity Diagnostics
LOWESS, GAM smooths, turning-point detection
Residual Structure
Distribution shape, partial residuals, added-variables
SHAP Interpretability
Dependence paths, global feature importance
Temporal Validation
Expanding-window CV, RMSE curves, bootstrap CIs
Validated Analytical Artifacts
Diagnostics, figures, logs, reproducible metadata
The system applies five parallel diagnostic modules—nonlinearity analysis, influence assessment, residual structure evaluation, SHAP-based interpretability, and temporal validation—to ensure that model outputs are structurally stable, interpretable, and robust under heterogeneous macroeconomic conditions.
Core Results Summary
Comprehensive empirical findings at a glance
Loading visualization...
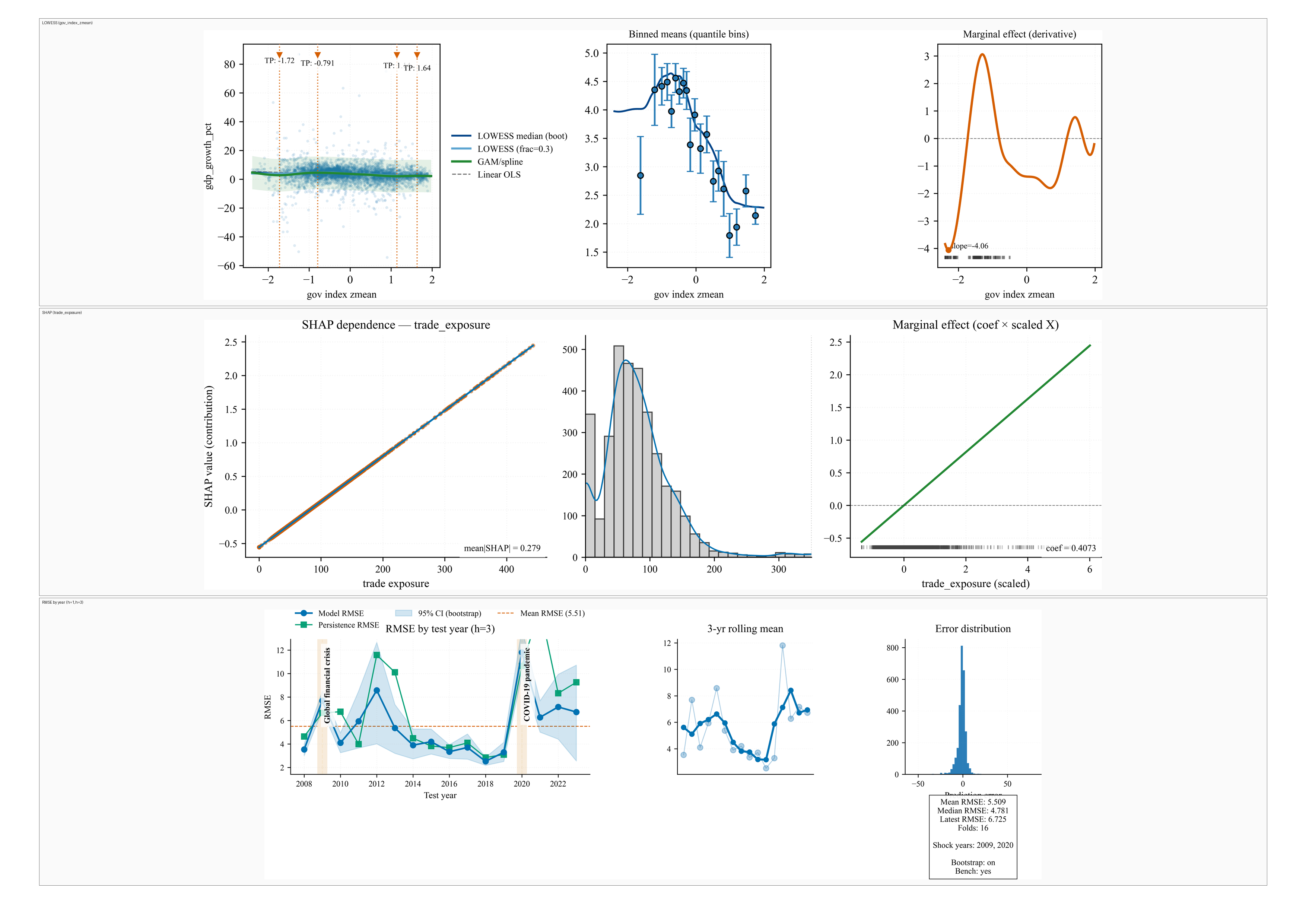
This composite summarizes the core empirical behavior of the proposed hybrid machine learning–econometrics system. Nonlinearity diagnostics (LOWESS and binned means) reveal smooth, stable relationships, with governance exhibiting curvature consistent with short-run reform effects rather than instability. SHAP dependence and coefficient-based marginal effects jointly confirm a strong, monotonic contribution of trade exposure, validating cross-method interpretability. Rolling out-of-sample forecasting demonstrates stable performance outside global shock periods, with well-behaved error distributions, indicating robustness, temporal stability, and absence of overfitting.
Plot Explorer
Select a category to view diagnostic plots and visualizations
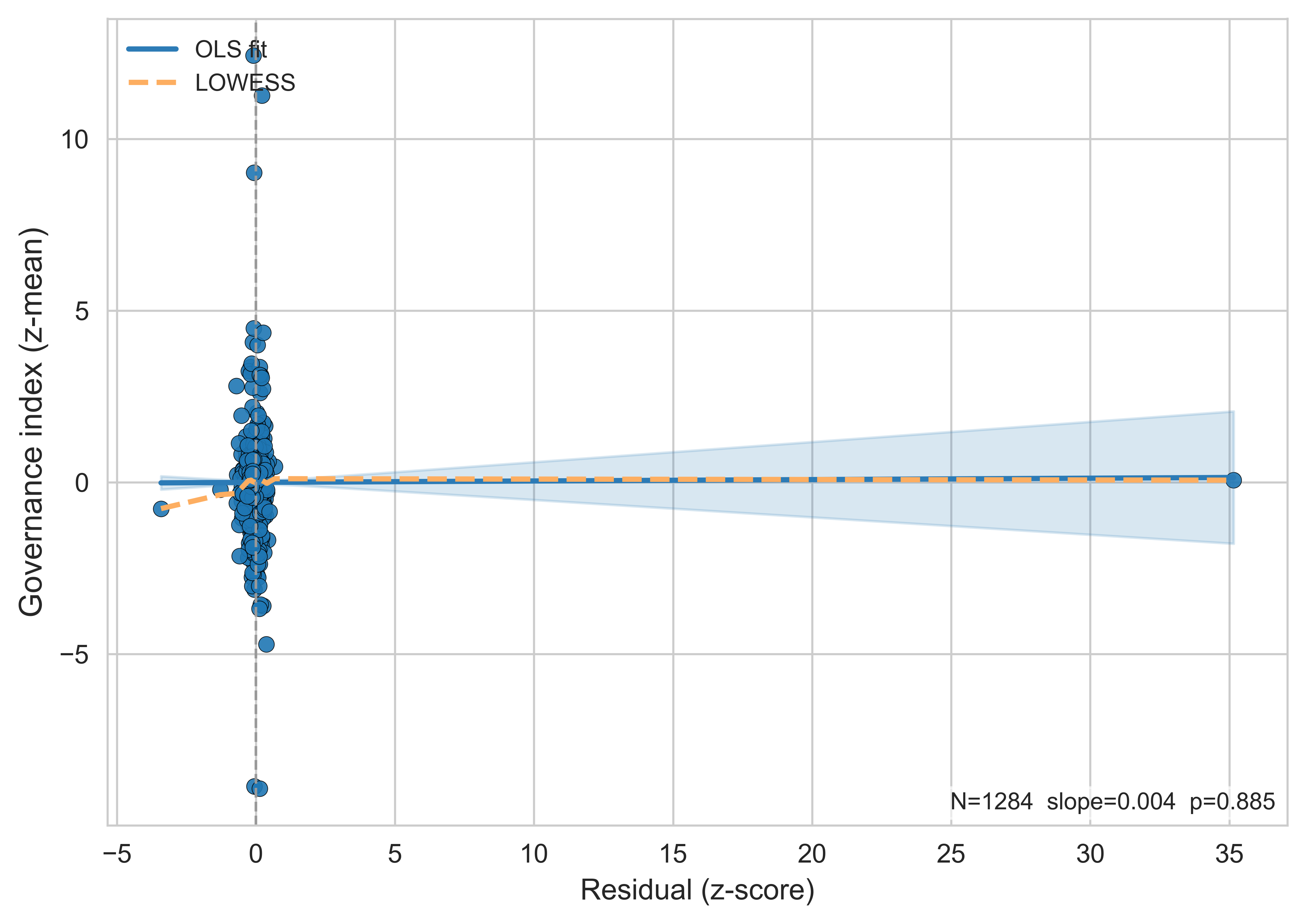
Government Index
Residual diagnostics show no systematic relationship between governance and model errors: both OLS and LOWESS fits are flat with an insignificant slope (p = 0.885). This indicates no residual structure or misspecification linked to governance.